1. Change History
4.2.1 (14. Nov 2025)
-
When receiving a SIP INFO request with unknown content a 200 OK response will be sent to ensure calls don’t get terminated
-
Changes to customer specific interface
4.2.0 (07. Jul 2025)
-
Changed behavior when receiving a 408 Timeout SIP response: Call will not get terminated anymore
4.1.0 (03. Jun 2025)
-
Added an updated inband modem worker implementation based on PJSIP. Worker implementation in use can be switched on the system configuration page. For the time being the legacy implementation stays the default
4.0.2 (16. Apr 2025)
-
EN16102: Fixed WSDL output to contain correct service URL when running behind a reverse proxy
-
Enhanced SIP INVITE for PSAP callback in NG eCall scenario by adding Priority, Accept, and Recv-Info headers (according to 3GPP TS 24.229 V19.2.0 clause 5.1.6B).
4.0.1 (24. Jan 2025)
-
Fixed start.sh script to point to /etc/ecall-router4-application.properties
-
Added parameter
no-waitto/callIvs- Network interfaces v.1.14
4.0.0 (01. Sep 2024)
-
Modernized user interface, added dark mode
-
Added support for Ubuntu 24.04 and Asterisk 20.7.0
3.12.0 (12. Jul 2024)
-
Added "Block All Incoming Calls"
3.11.0 (17. May 2023)
-
Added X-Proxy-Group-Name to configure group assignment of incoming operator calls
-
Added support to copy SIP headers from operator INVITE to IVS INVITE
3.10.0 (20. Mar 2023)
-
Extended "eCall Center controls AL-ACK" feature
3.9.0 (06. Mar 2023)
-
Fixed MSD decoding with missing vehicle direction
-
Fixed Asterisk crash on early NG MSD retransmission
-
Added worker on demand feature
3.8.0 (08. Dec 2022)
-
Added eCall mode for inbound calls
3.7.0 (11. Oct 2022)
-
Added support for persistent block list
-
Network interfaces v.1.12
3.6.0 (23. Mar 2022)
-
Upgrade to Asterisk 16.24.1
-
Network interfaces v1.11
3.5.0 (11. Jan 2022)
-
Added allow list feature
-
Network interfaces v1.9
3.4.0 (27. Oct 2021)
-
Added support for MSDv3
-
Network interfaces v1.8
3.3.0 (10. Aug 2021)
-
Added support for EN16102 (license restricted)
3.2.0 (20. Apr 2021)
-
Added support for incoming operator calls (see chapter 12.2.3.2 for details)
-
Added support to copy SIP headers from incoming call to operator call
3.1.0 (26. May 2020)
-
eCall Mode group configuration option only affects outbound calls
-
Fixed initial map display on dispatch page
-
Made MSD retransmissions more robust against CRC errors
3.0.0 (31. Mar 2020)
-
Support for Next Generation eCall
-
License Keys
-
Workstation Phone Number on Dispatch is saved per user
2. Introduction
This document describes the user interface of the eCall Router. To access the user interface a web browser with activated JavaScript is required. The following browsers are supported:
-
Google Chrome
-
Mozilla Firefox
-
Microsoft Edge
3. References
[1] eCall Router – Network Interfaces v1.14
[2] Intelligent Transport Systems – ESafety – eCall high level application requirements (HLAP), CEN/TC 278, EN 16062
4. Login Page
To login to the system a web browser is required. Enter the URL
http://<server-ip-address> into the address bar of your browser. The IP
address has to be replaced by the actual configured IP address of your
eCall Router.
You will then be asked to enter the login password. The standard user and password on delivery are admin and 1234.
5. Calls Page
After login you will be redirected to the calls page.
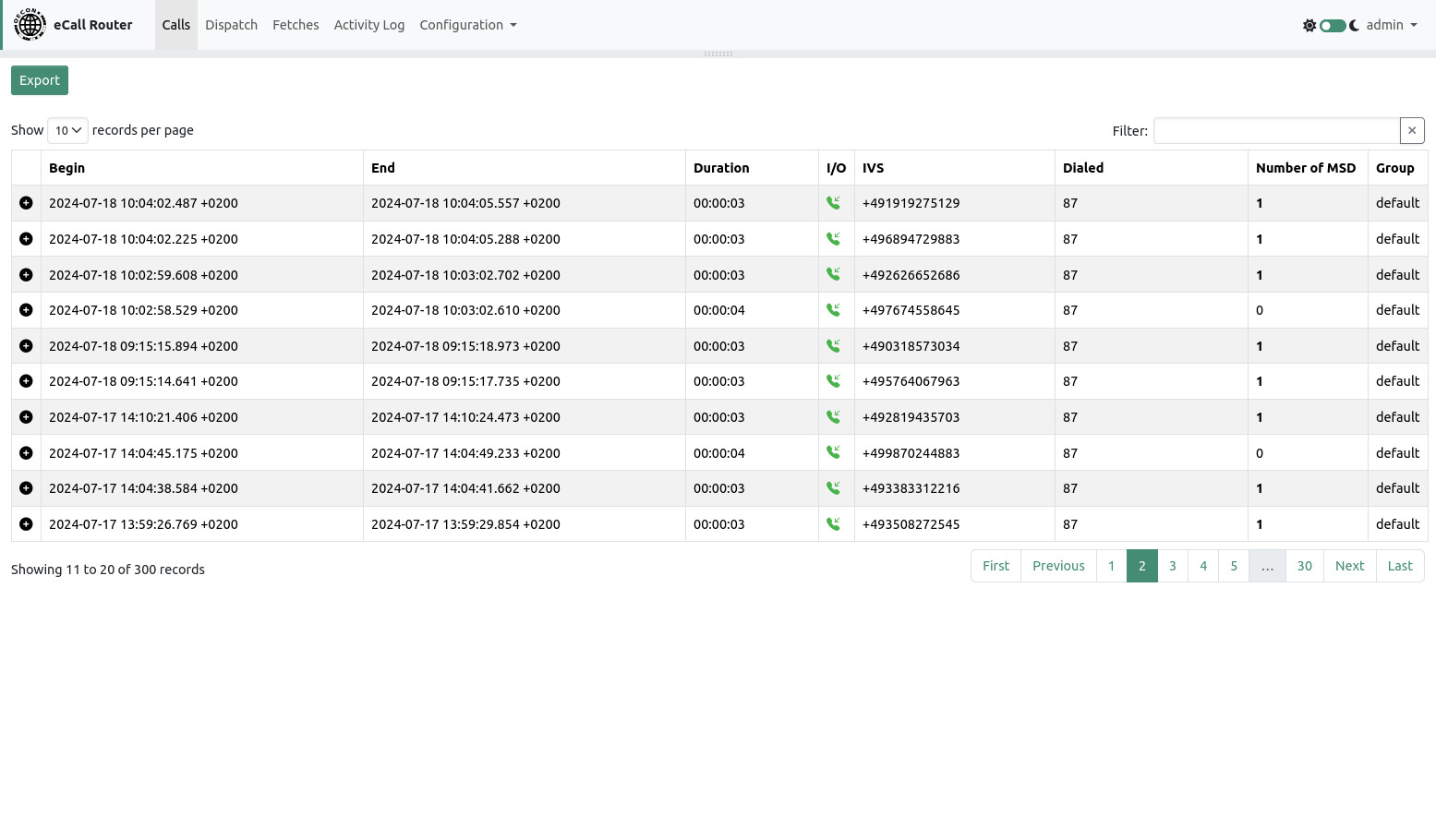
On this page you can find a table of all calls that the eCall Router has processed so far. For every call you can see the time of begin and end, the duration, incoming or outgoing call, the phone number of the calling IVS, the dialed number (only for incoming calls), the number of MSD that were transmitted during the call and the group to which the call has been assigned.
The calls are ordered by the time of their arrival from new to old.
To left of each call is a plus icon that can be clicked to expand a text area with additional information of the call. If one or more MSD were transmitted they will be decoded and shown here.
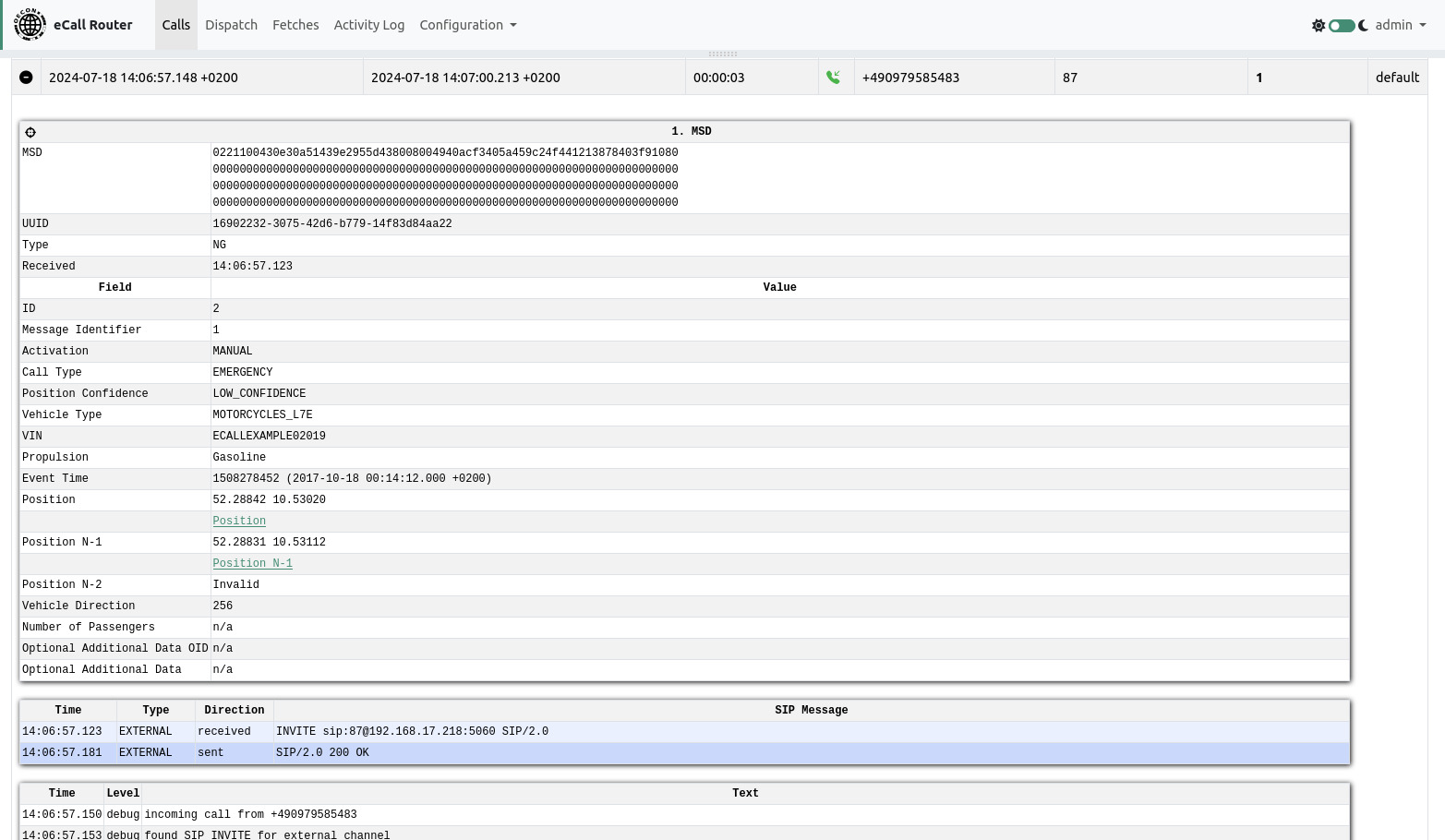
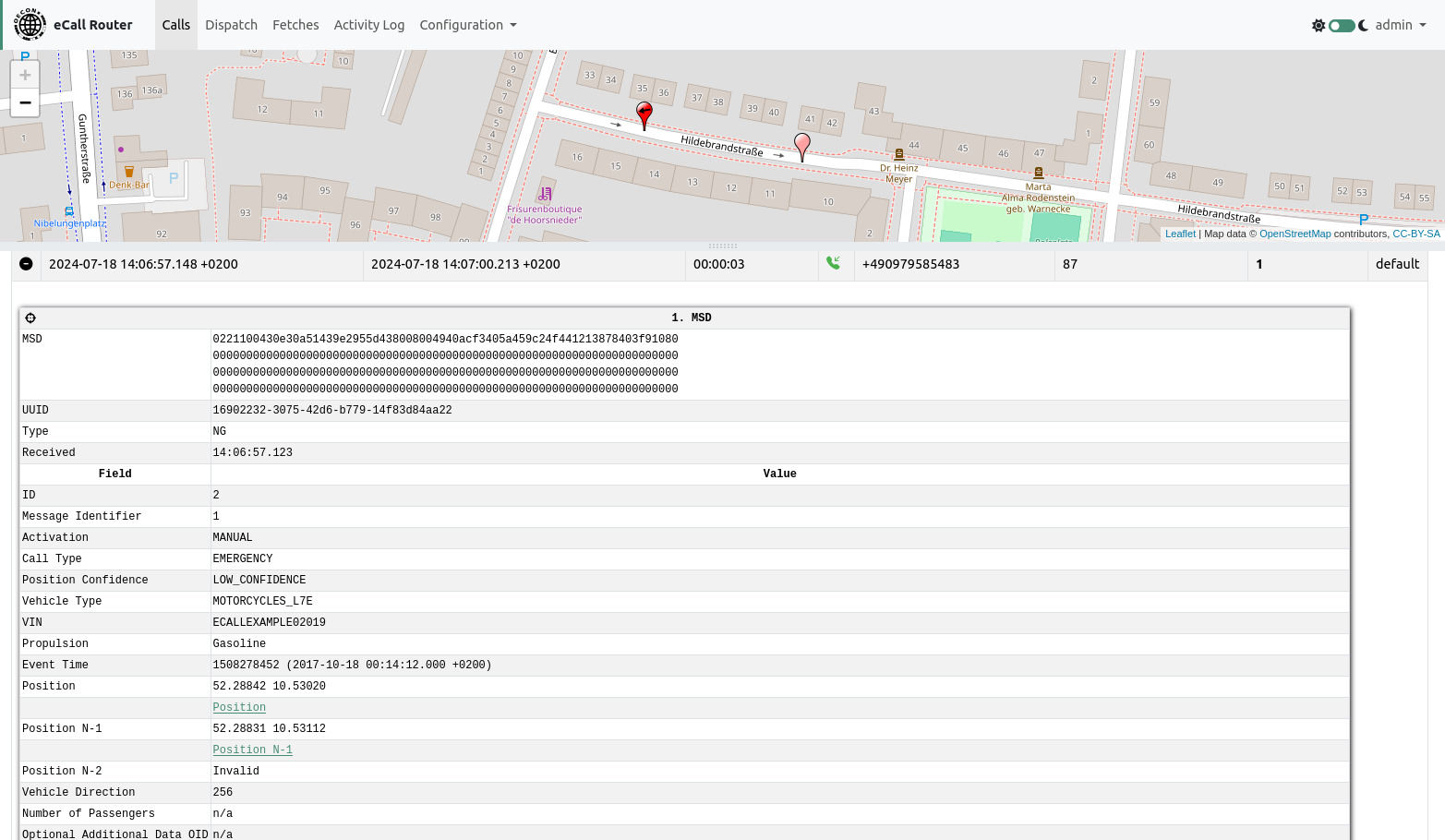
The top of the calls page contains an expandable map. You can drag it down with the gray bar just below the navigation bar if it is not visible. To display an MSD’s position on the map you can click the crosshair icon on the left side of the MSD panel.
The filter to top right of the table can be used to show only calls from a specific phone number.
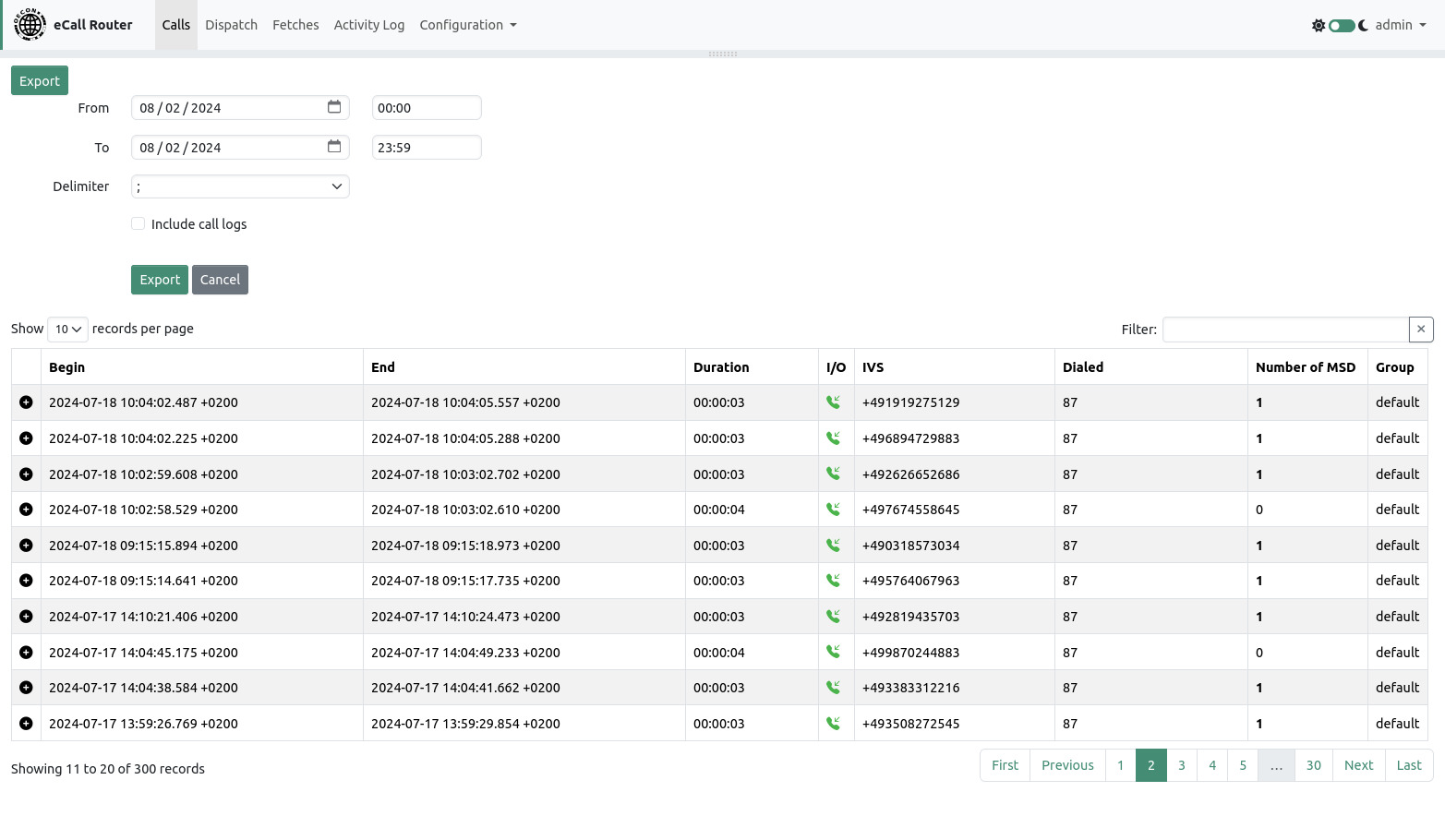
The export function can be used to export calls and MSDs as a CSV file. If the “Include call logs” checkbox is ticked then the complete call debug log will be included as a multiline field in the CSV file. If a filter is active then the filter value will also be taken into account for the export.
6. Dispatch Page
The dispatch page shows active and recent calls and the last received MSD for each call. Calls that ended more than 5 minutes ago will be removed from the call list at the top left of the page. The amount of time can be configured on the configuration page. The currently selected call will not get removed as long as the page is not being reloaded or a new call is coming in.
The admin user can see every call that the eCall Router processes, ordinary users can only see calls that belong to their respective groups.
Buttons below the map list allow a user to request a MSD, to send an application layer cleardown, to call an IVS or to hang up an active call.
Besides the IVS phone number calling an IVS requires the user to enter a workstation phone number to ensure that the call to IVS gets forwarded to the correct workstation.
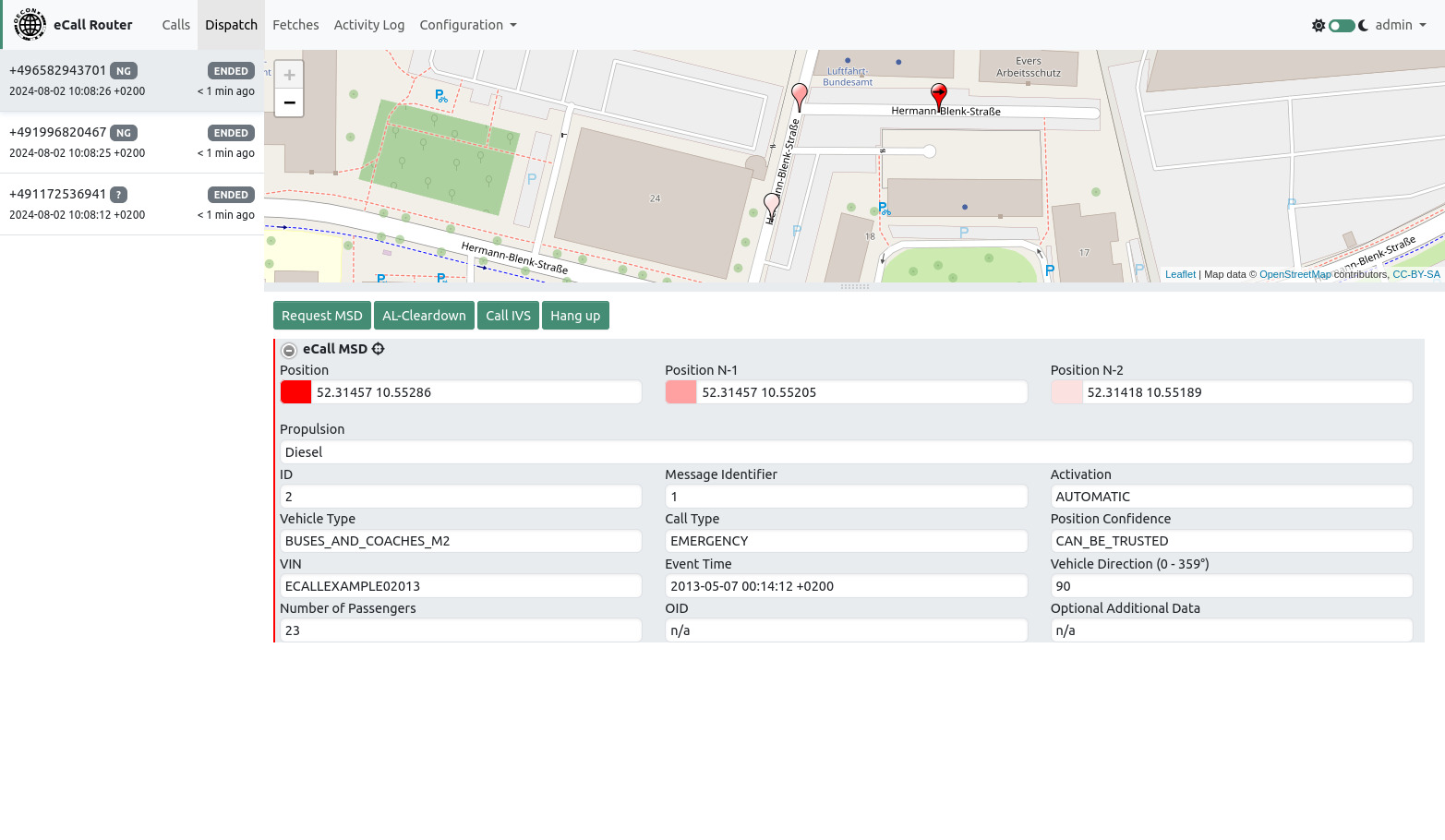
If VIN decoding has been enabled on the system configuration page then additional information is being shown below the decoded MSD fields.
7. Fetches Page
On this page every fetch of a workstation (see [1]) is recorded. This page is only visible if you are logged in as the admin user.
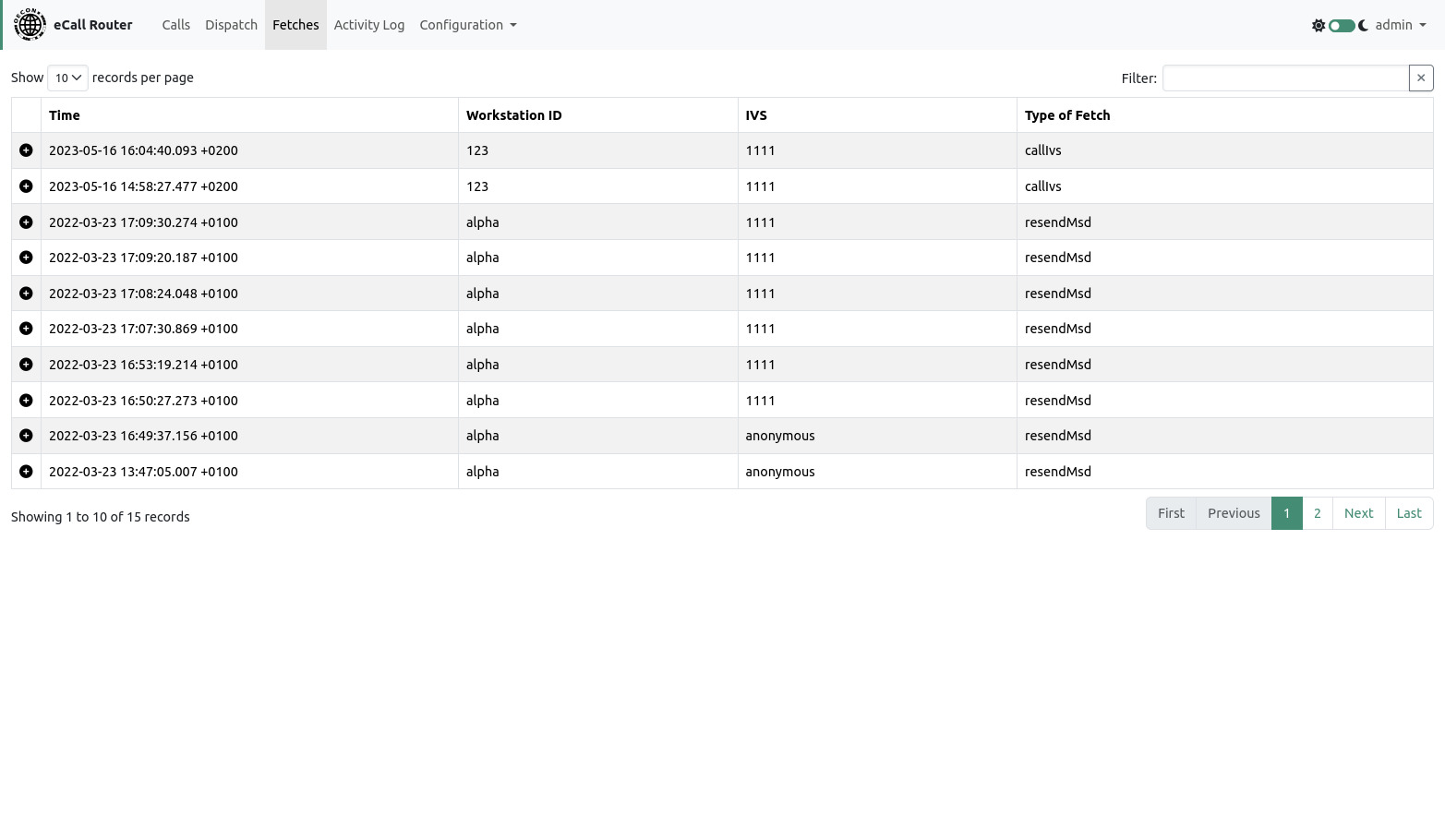
Like on the calls page you can get additional information by clicking on the plus sign on the left of a row or use the filter to show only records concerning a specific phone number.
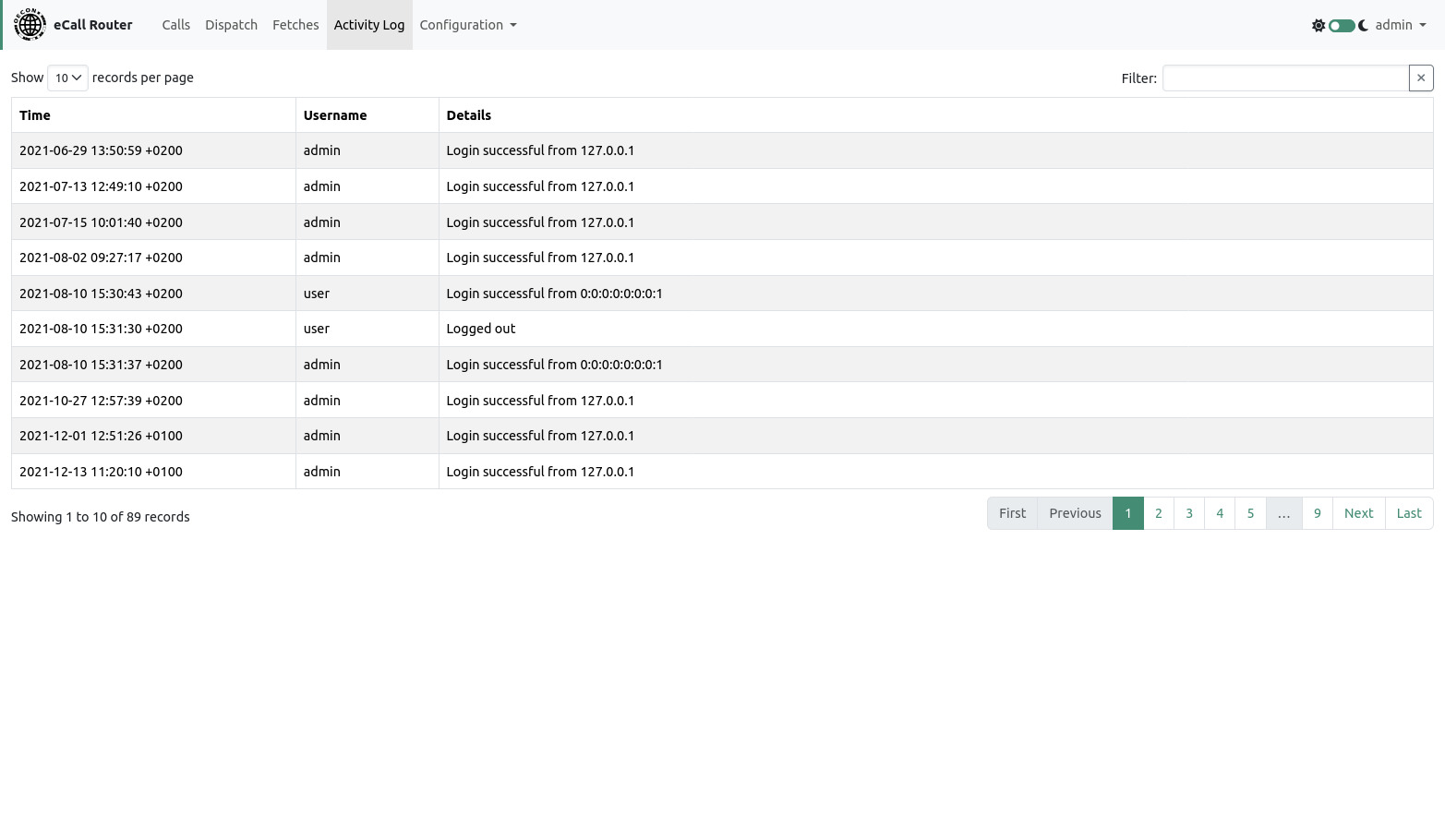
8. Activity Log
On this page the activity log of the system is shown. The activity log contains information about user actions including login, logout and downloading of audio call recordings. The page is only visible to the admin user.
9. Users
This page allows viewing, adding, editing and locking user accounts. A new user can be created by clicking the link at the top of the page. Every user has to be assigned to a group. A user may only see calls that belong to his group.
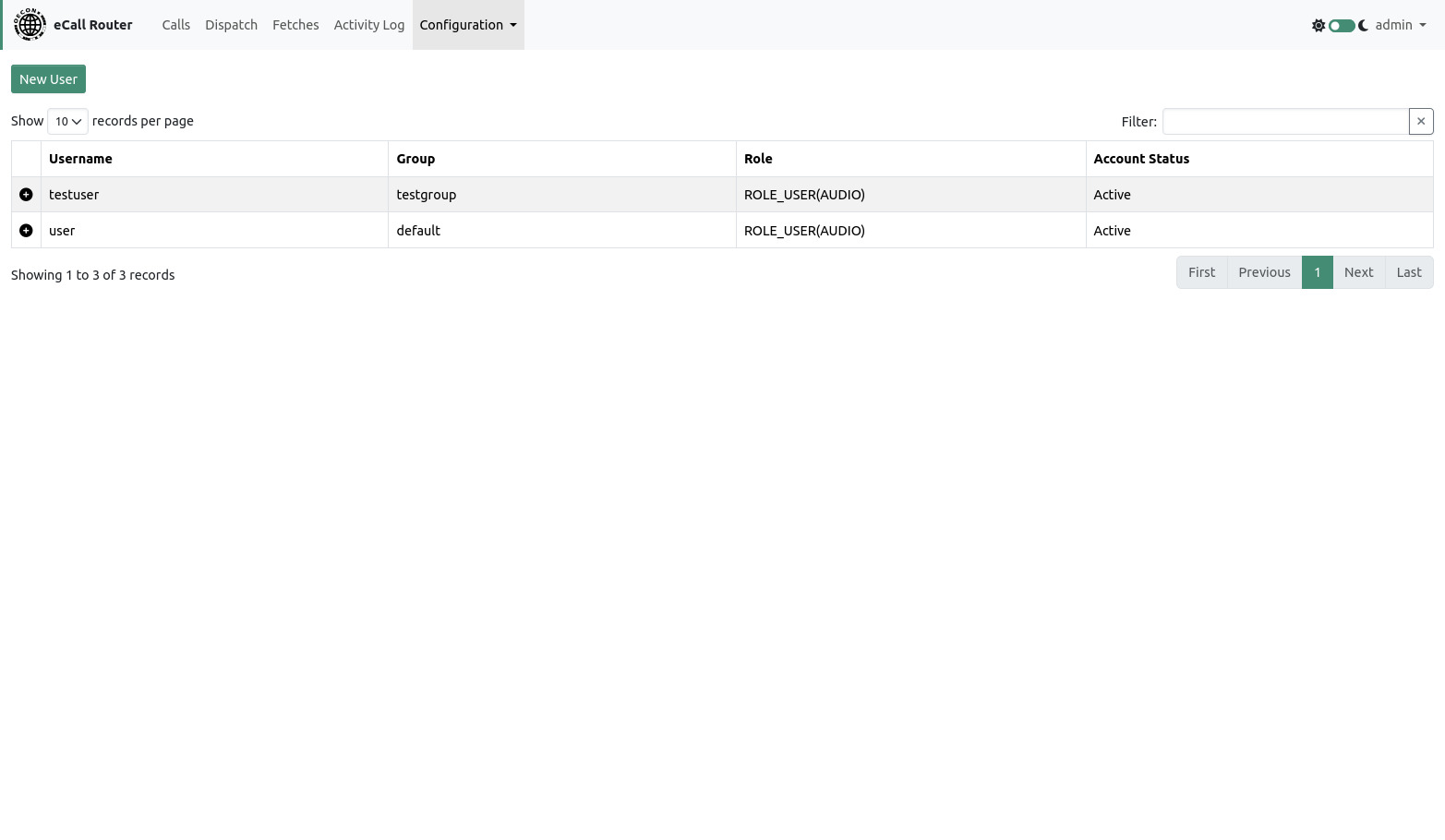
Only users with the „Download audio call recordings“-permission are able to see and download call recordings from the “Calls” page.
10. Groups
This page allows viewing, adding and editing groups. A default group called default exists on delivery. New groups can be created by clicking the link at the top of the page.
Configuration options per group can be expanded by clicking the plus sign next to the group in the table.
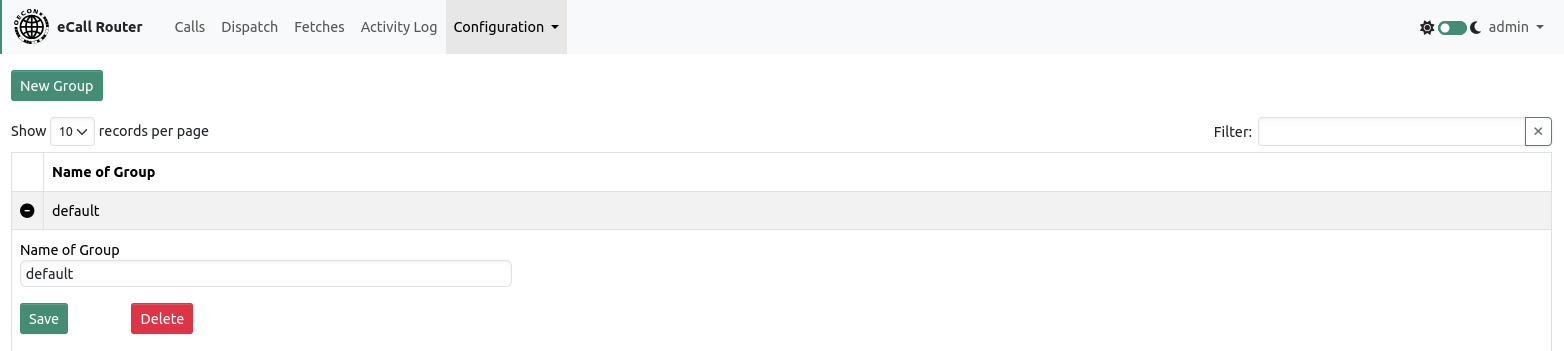
The name of a group can be chosen freely but must be unique. The default group may be renamed but it will still always be the default group. Deleting a group will also delete all associated users and calls. The default group cannot be deleted.
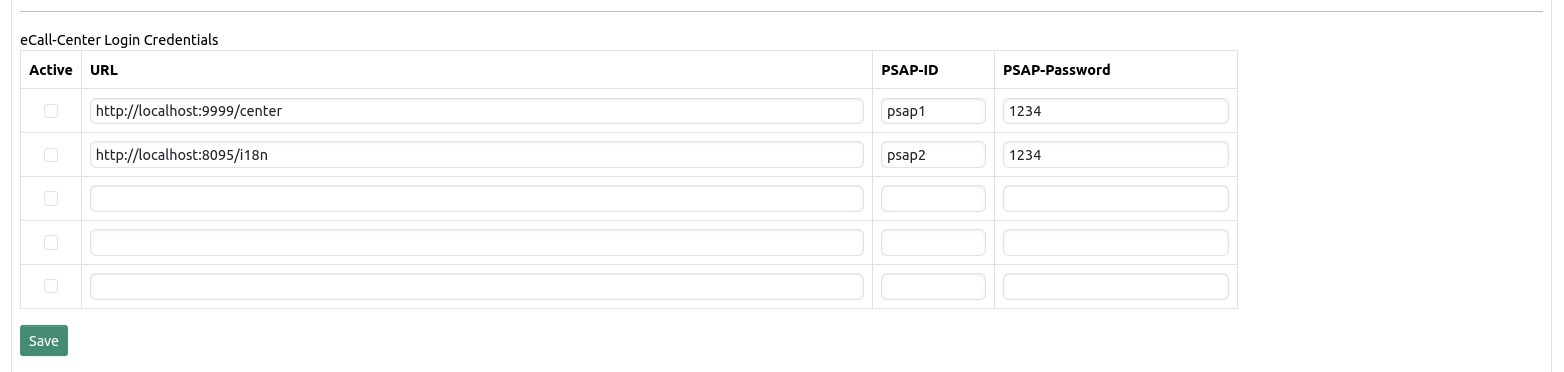
You can configure up to five eCall Centers. See [1] for additional information on eCall Center and data transmission procedures. Note that you don’t have to configure an eCall Center here. If no eCall Center is configured or reachable you will just have no additional information to a MSD that could be provided by the eCall Center.
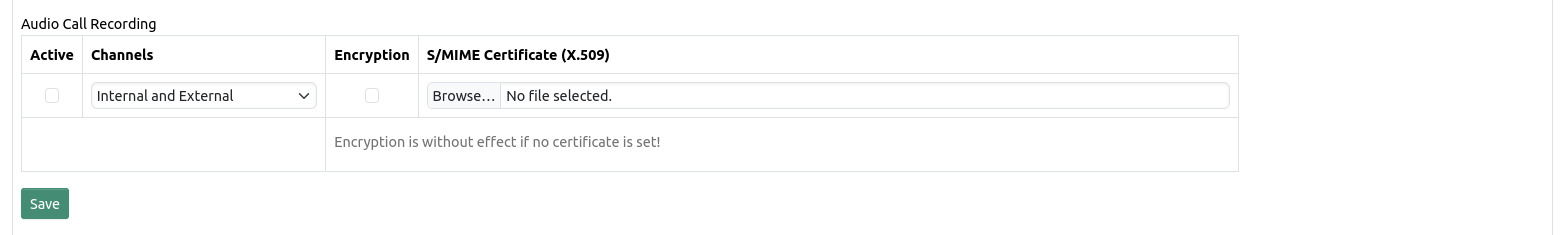
Audio call recording can be enabled per group. The “Channels” setting determines the extent of the recording. Internal only means that only audio of the agent will be recorded, external only means that only audio of the calling IVS will be recorded, while Internal and External means that both channels will be recorded and mixed into a single WAV file.
Encryption can be enabled to encrypt all audio files that are being recorded by the eCall Router. Besides setting encryption to “enabled” you also have to upload a X.509 S/MIME certificate for the encryption feature to work. The public key contained within the certificate will be used for encryption so that only the owner of the corresponding private key will be able to decrypt a call audio recording.
Note: Audio call recording requires appropriate Asterisk configuration which is not enabled by default (see Audio call recording)

In these two sections SIP headers can be defined which will be copied from either an incoming IVS INVITE to an outgoing operator INVITE or from an incoming operator INVITE to an outgoing IVS INVITE.
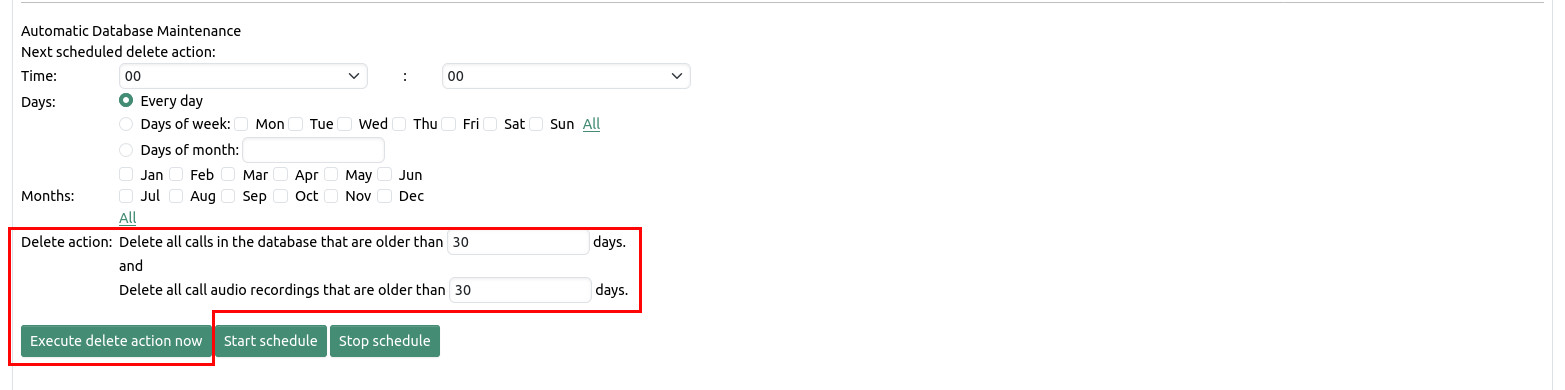
Using the delete function calls can be permanently removed from the database. Possibly existing audio recordings will be removed from the file system.
The manual delete action is called by clicking the "Execute delete action now" button. After confirmation by the user all calls are deleted from the database that are older than the specified number of days and all call recordings are deleted from the file system that are older than the specified number of days. Note that deleting a call from the database must also delete the associated call recording which is why the second number of days has to be less than or equal to the first number of days.
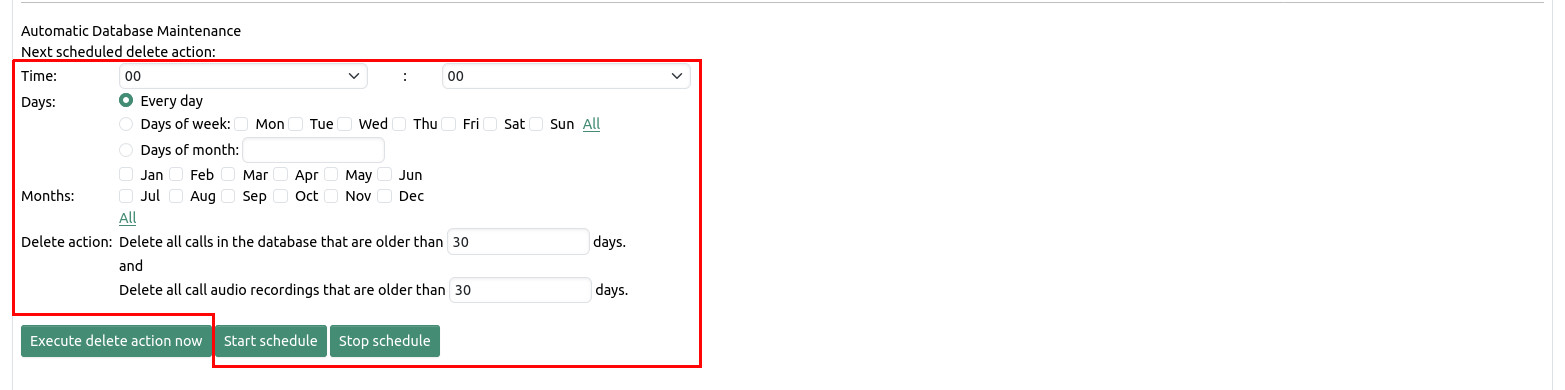
The scheduled delete action allows you to create a schedule to run periodically delete operations. A schedule includes the specification of a time, a daily selection, a selection of months, and the age of calls (in days) that are to be deleted during the execution of the operation. After clicking on the button "start schedule" the set values are accepted and the time of the next scheduled deletion is being displayed.
A scheduled delete action can be cleared by clicking the "stop schedule" button.
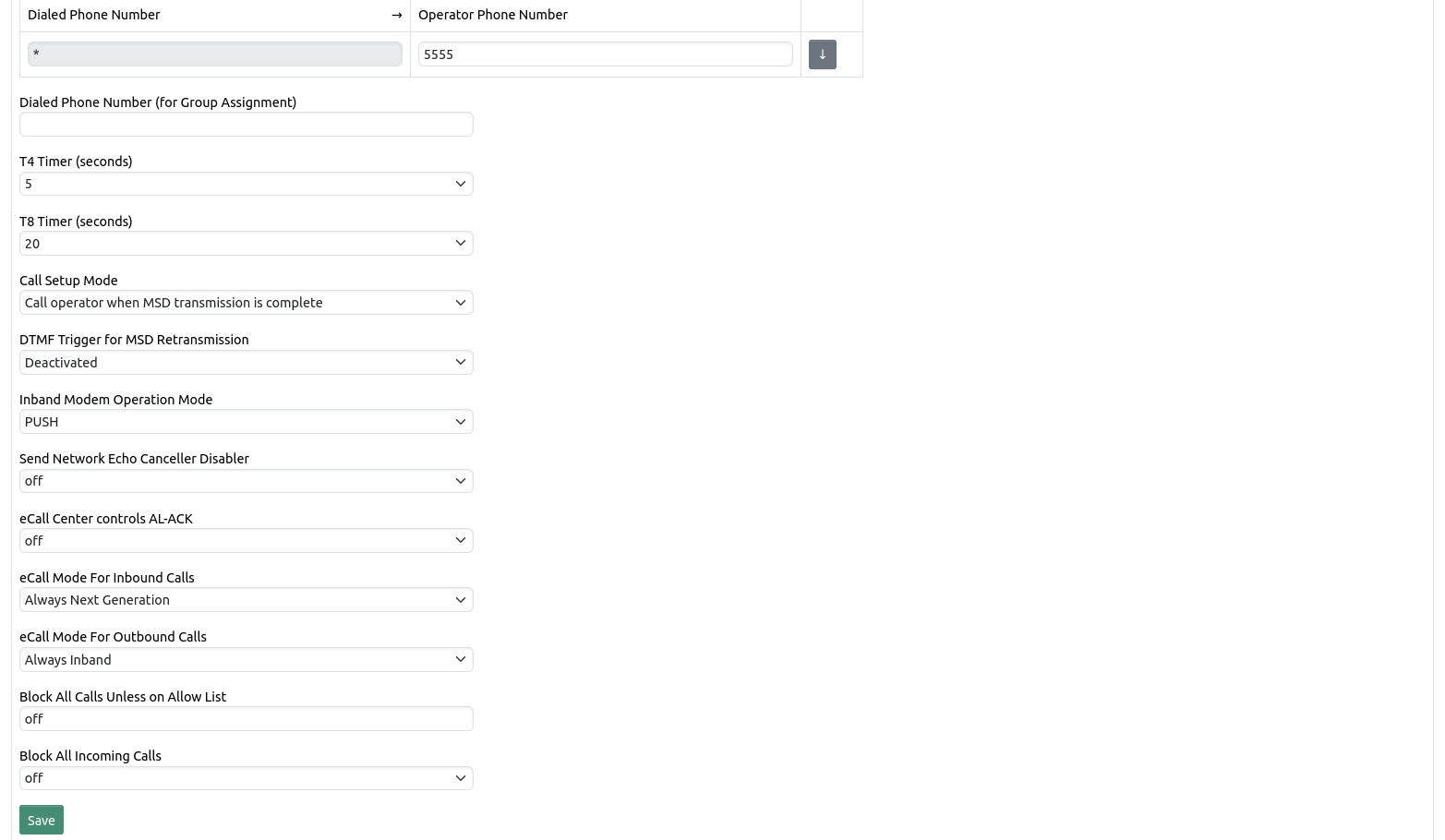
The operator phone number determines which phone number gets called when the eCall Router has to forward an incoming call to a human dispatcher.
Dialed Phone Number expects a POSIX regular expression to be matched against the called phone number of an incoming call and determines to which group the incoming call will be assigned. It is best to leave this setting empty for the default group as the default group will always be used as a fallback when no other group matches.
The parameters T4 timer and T8 timer define certain timeouts that may be triggered during a MSD transmission. The meaning of the parameters is described in [2].
The call setup mode can be changed to forward calls immediately to the respective operator phone number (described above) or to wait for the initial MSD transmission to complete. Note that the human dispatcher will hear nothing and will not be able to speak during a MSD transmission.
The parameter “DTMF Trigger for MSD Retransmission” can be used to request a MSD retransmission upon detection of the configured DTMF (Dual-tone multi-frequency) signal. During an ongoing call the human dispatcher can generate a DTMF signal using his telephone keypad. A received MSD will be acknowledged with a positive acknowledgement.
The parameter “Inband Modem Operation Mode” can be used to switch between PUSH and PULL mode. In PUSH mode the inband modem waits until the initiation signal of an IVS is detected before sending the MSD request. In PULL mode the inband modem immediately starts to send the MSD request after call establishment.
Setting the parameter “eCall Center controls AL-ACK” to “on” means that the eCall Router will only send ACKs during In-band modem transmission if the response of the eCall Center to the saveMsd request contains a HTTP header “Send-AL-ACK” that is set to “true”. If it is found to be set to “false” then no ACK will be sent, the call will be hung up immediately and all calls from the calling IVS will be blocked for the next few minutes. Note that this setting is a deviation to the European eCall standard. If the parameter is set to “on (also check allow list if SIP INVITE contains no NG MSD)” then NG MSDs that are found in an SIP INVITE will be transmitted to the eCall Center before the call is accepted. If the “Send-AL-ACK” header is set to “false” the call will be declined, otherwise the call will be accepted. Also, if no NG MSD is found in the SIP INVITE then the allow list will be checked and the call will only be accepted if the IVS phone number is on the allow list.
eCall Mode For Inbound Calls affects only incoming calls. The default setting is “Try Next Generation with fallback to Inband” which will try to find a MSD inside the initial SIP INVITE and if it doesn’t find one will activate the inband modem. “Always Next Generation” will never activate the inband modem and only look for MSDs inside the SIP INVITE. “Always Inband” will always activate the inband modem and ignore data inside the SIP INVITE.
eCall Mode For Outbound Calls affects only outgoing calls. The default setting is “Always Inband” which means only inband modem MSD transmissions are activated. Setting it to “Always Next Generation” means only MSD transmissions through SIP INFOs are being used. ”Try Next Generation with fallback to Inband” means that first a SIP INFO will be sent to request a MSD, only if this is unsuccessful the inband modem will be activated. “IVS phone number database lookup with fallback” will check the last received MSD from the call database and set the mode accordingly, if there has been no MSD received yet from the IVS phone number in question the behavior is like “Try Next Generation with fallback to Inband”.
Setting the parameter “Block All Calls Unless on Allow List” to “on” means that the eCall Router will only accept incoming calls if the IVS phone number is currently on the list of allowed numbers. An IVS phone number can be added to the allow list through the Network Interfaces API. Any phone number added to the allow list will be automatically removed after 5 minutes.
With setting „Block All Incoming Calls“ all incoming calls can be rejected either with a busy signal (486) or a declined signal (603). This setting has a higher priority than the allow list, which means a call will be rejected even if the IVS phone number is on the allow list.
11. System Configuration Page
On this page various system configuration options can be changed.
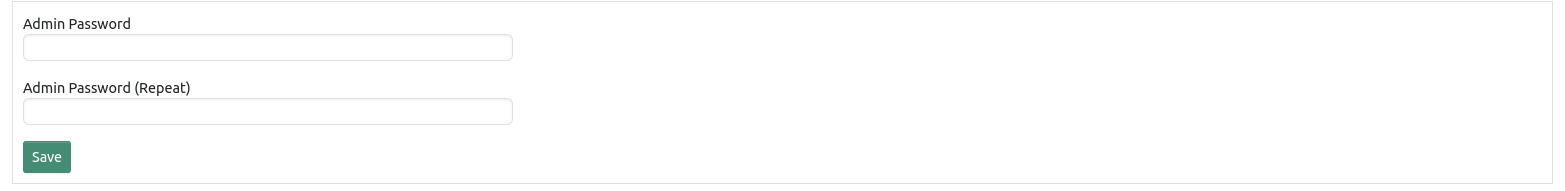
To change the admin password enter the new password twice and click the save button below.
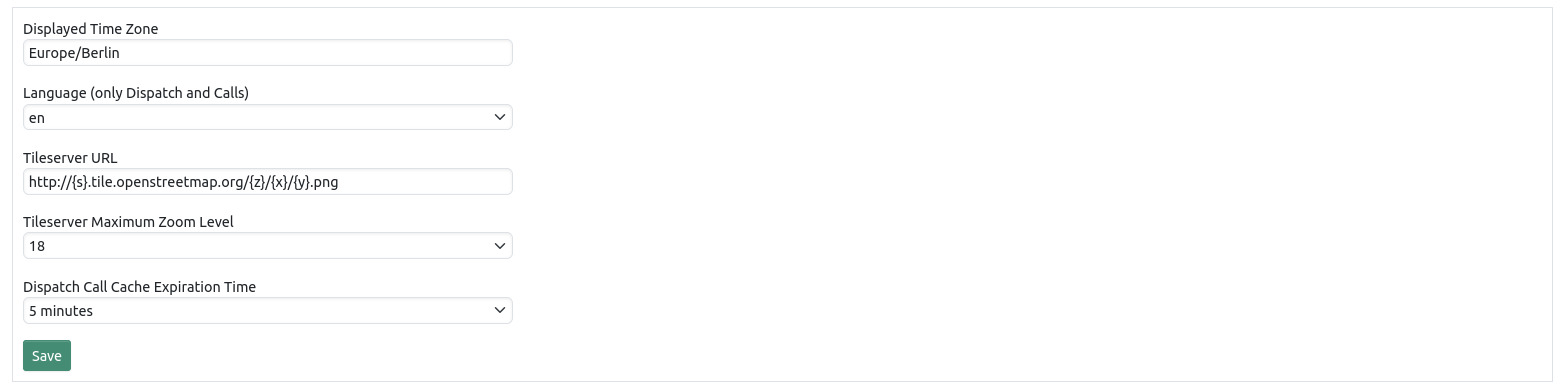
You can change the displayed time zone here. This affects all time stamps on all pages.
The language setting affects only the language on the calls and dispatch pages.
You can also change the URL of the Tileserver that provides the map on the dispatch and calls pages.
Changing call cache expiration time affects how long calls are being displayed on the dispatch page.
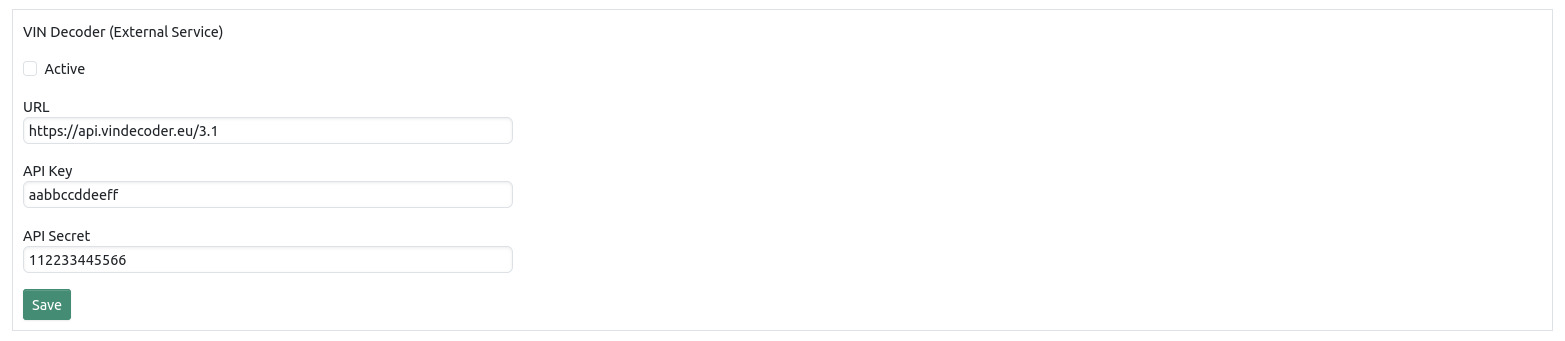
To enable the VIN decoder on the dispatch page you have to create an account at https://vindecoder.eu and request an API key and secret. The VIN decoding feature on the dispatch page can only work if your browser has internet access.
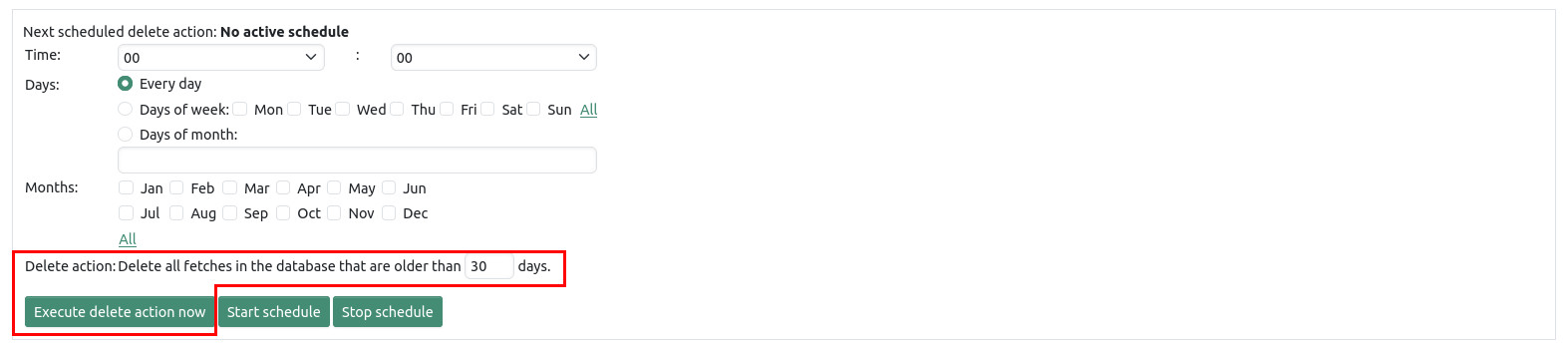
Using the delete function data can be permanently removed from the database.
The manual delete action is called by clicking the "Execute delete action now" button. After confirmation by the user all fetches are deleted that are older than the specified number of days.

The scheduled delete action allows you to create a schedule to run periodically delete operations. A schedule includes the specification of a time, a daily selection, a selection of months, and the age of calls (in days) that are to be deleted during the execution of the operation. After clicking on the button "start schedule" the set values are accepted and the time of the next scheduled deletion is being displayed.
A scheduled delete action can be cleared by clicking the "stop schedule" button.

You need a valid license key to run eCall Router (Version 3 and up). Please copy and paste the license key you have been sent from OECON P&S Support in the text field in this section. The software will instantly show the Licensee and the expiration date of your license once you press the Save button.
Without a valid license key installed eCall Router will show a red banner on every page.
The software will still receive and save eCalls without a valid license but you can’t see call details or decode MSDs. As soon as a valid license key is entered you can inspect all previously recorded calls.
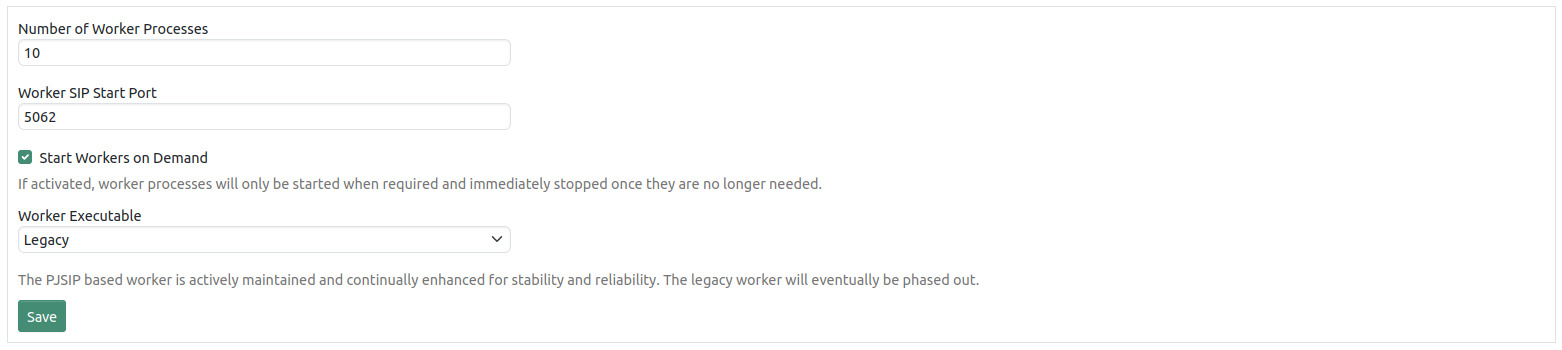
The parameters “Number of Worker Processes” and “Worker SIP Start Port” depend on the type of telephony hardware of the eCall Router. Usually there is no need to change them. In the default configuration all workers are started when the systems starts and they will keep running as long as the system runs. It also possible to switch to an on demand mode. In this mode a worker will only be started once it has been requested and stopped once it is not needed anymore. The on demand mode therefore provides better resource utilization.
You can switch between the legacy worker implementation and the PJSIP worker implementation. The latter one is actively maintained and continually enhanced for stability and reliability. The legacy worker will eventually be phased out but stays the default choice for the time being.

For troubleshooting purposes, it is possible to access the internal log files of system through the web interface. Use of this function is not required during normal operation.

With the “reboot system” button, the system can be restarted. The system takes about 30 seconds to return to operational state.
With the “shutdown system” button, the system can be shut down. You need physical access to the device to turn the system back on.
12. Geofencing
The Geofencing feature allows choosing different operator phone numbers according to the MSD position of the caller. If the MSD could not be received or the position is outside of all geofences then the eCall Router will fall back to the configuration from the miscellaneous section of the group configuration page.
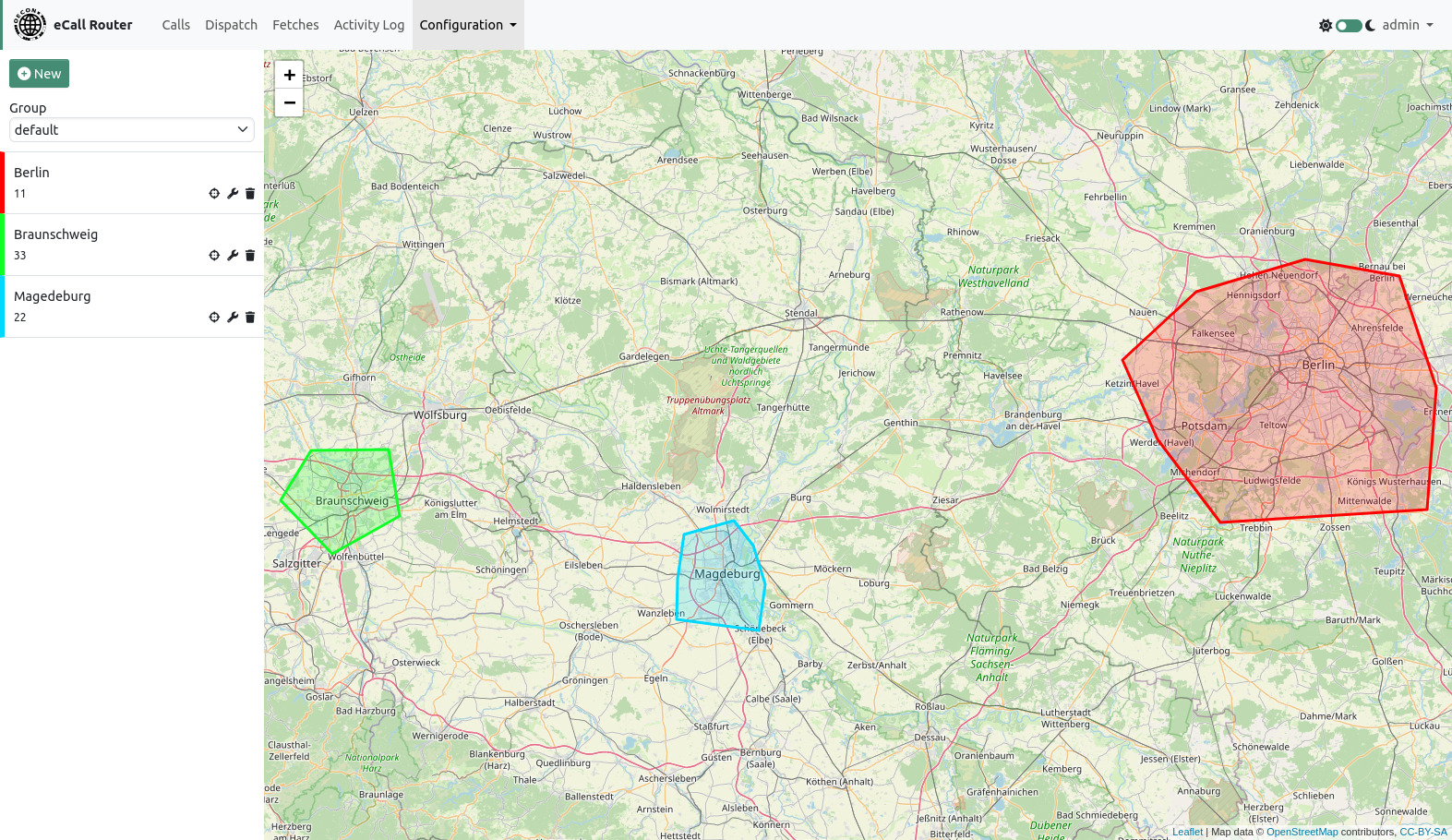
The geofencing page shows all geofences for the currently selected group on a map.
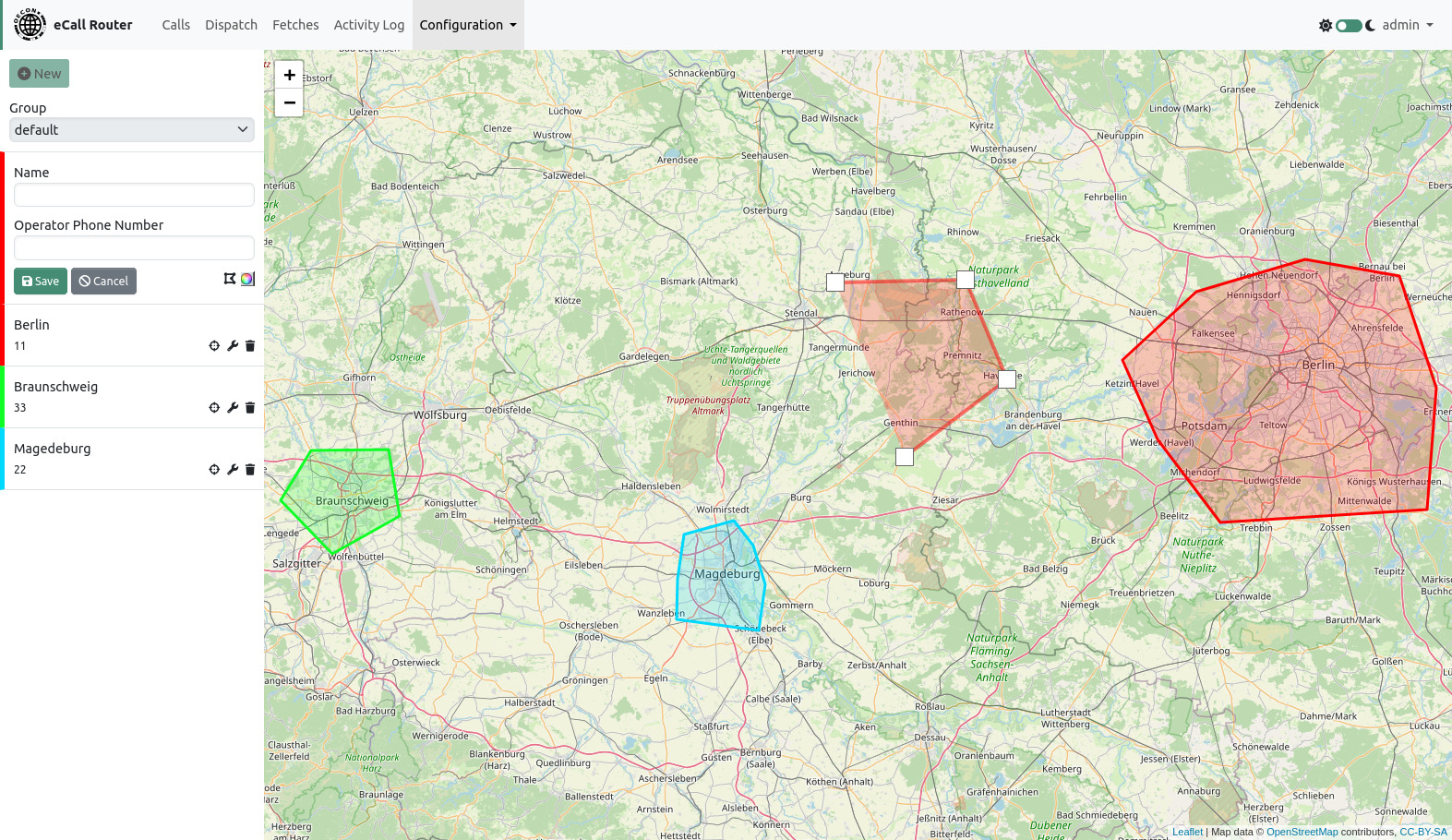
Create a new geofence by clicking the “New” button. Enter a name and an operator phone number. Then create a polygon on the map by clicking on the map. Close the polygon by clicking on the first point. You can change the color of the geofence by clicking on the color picker icon.
You can center, edit or delete a geofence by clicking on the buttons next to the name in the list of geofences on the left site of the page. When editing a geofence you can delete points by clicking on them and create new points by dragging the half transparent points between two existing points.
13. Server Administration
Server administration tasks have to be executed over a SSH connection. The SSH service is active by default on every eCall Router installation. The default user for administration tasks is ecall. On Ubuntu this user is allowed to use the sudo command to execute commands with root privileges. All of the following command should be executed with root privileges.
13.1. Components
The system components that are required to run:
-
Asterisk
-
Apache HTTPD
-
PostgreSQL
All these components are automatically getting started when the system is being booted.
13.2. Asterisk
Asterisk is used for all external call handling and connects external calls to the eCall Router process that does call handling using Asterisk’s ARI interface.
13.2.1. Starting, stopping, restarting Asterisk
service asterisk <start | stop | restart>
13.2.2. SIP configuration
SIP configuration can be found in /etc/asterisk/pjsip.conf and will be
generated by the setup program.
13.2.3. Dial plan
The dial plan is configured in /etc/asterisk/extensions.conf. For
inbound calls there is a section that forwards these calls to the ecall
application (usually in a context named default-in):
[default-in]
exten => _[a-zA-Z.:0-9+].,1,NoOp()
same => n,Set(CALLERID(num)=${IF($[ ${LEN(${CALLERID(num)})} > 0 ] ? ${CALLERID(num)} : anonymous)})
same => n,Set(audiofile=${SHELL(uuidgen -r):0:36})
; same => n,Monitor(,${audiofile},m)
same => n,Stasis(ecall,${audiofile})
Audio call recording
To enable call recording of incoming calls the dial plan has to be adjusted. Each line containing “Monitor” must be enabled by removing the leading semicolon. For example:
; same => n,Monitor(,${audiofile},m)
to
same => n,Monitor(,${audiofile},m)
The default configuration contains three lines containing “Monitor” that must be enabled.
Incoming operator calls
By default all incoming calls will be regarded as calls from an IVS. If
a call shall be regarded as a call from an operator then it is necessary
to set the channel variable X-Proxy-To-External before calling the
stasis app.
The value of the channel variable must be the phone number that will be used for the outgoing call to the IVS.
In this example the incoming call from the operator is handled by the
from-operator context. The dialed number will be used in the outgoing
call to the IVS in context default-external-out. Note that from-operator
must be the configured context of the pjsip endpoint from which the
operator call originates:
[from-operator]
exten => _[0-9+]!,1,NoOp()
same => n,Set(X-Proxy-To-External=${EXTEN})
same => n,Stasis(ecall)
[default-external-out]
exten => _[0-9+]!,1,NoOp()
same => n,Set(audiofile=${X-Audio-File})
; same => n,Monitor(,${audiofile},m)
same => n,Dial(PJSIP/${EXTEN}@pbx)
It is also possible to use a different context for the outgoing call to
the IVS. In this case use phone-number@context as the value of
X-Proxy-To-External.
In this example the context from-operator-out will be used for the
outgoing call to the IVS:
[from-operator]
exten => _[0-9+]!,1,NoOp()
same => n,Set(X-Proxy-To-External=${EXTEN}@from-operator-out)
same => n,Stasis(ecall)
[from-operator-out]
exten => _[0-9+]!,1,NoOp()
same => n,Set(audiofile=${X-Audio-File})
; same => n,Monitor(,${audiofile},m)
same => n,Dial(PJSIP/${EXTEN}@pbx)
By default calls will be assigned to the default group. A variable
X-Proxy-Group-Name can be used to change this behavior. In this example
the calls will be assigned to a group named my-group:
[from-operator]
exten => _[0-9+]!,1,NoOp()
same => n,Set(X-Proxy-To-External=${EXTEN})
same => n,Set(X-Proxy-Group-Name=my-group)
same => n,Stasis(ecall)
13.2.4. Log files
Asterisk log files can be found in /var/log/asterisk.
13.2.5. Starting, stopping, restarting eCall Router application
service ecall-router4 <start | stop | restart>
13.2.6. Log files
The eCall Router logs can be found under
/usr/local/ecall-router-current/logs. This is the same log that can be
accessed using the web interface.
13.3. Apache HTTPD
The Apache HTTPD is used to deliver the web interface to the connecting clients. It uses mod_proxy to relay requests to the eCall Router application.
13.3.1. Starting, stopping, restarting Apache HTTPD
service apache2 <start | stop | restart>
13.3.2. Log files
The apache log files containing general information about HTTP requests
and responses can be found under /var/log/apache2/. Especially
access.log and error.log can be of interest.
13.4. PostgreSQL
All configuration and call data of the eCall Router is stored inside a
PostgreSQL database running on the same physical server as the eCall
Router itself. The name of the database is ecall_router4. The name of
the database user is ecall and the password is ecall. The user name and
password cannot be changed and access to the database is only possible
from localhost. The database can be accessed using the default command
line client psql. Backups of the database can be created using pg_dump.
13.4.1. Starting, stopping restarting PostgreSQL
service postgresql <start | stop | restart>